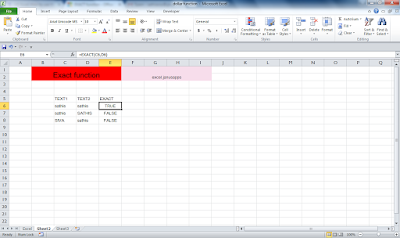
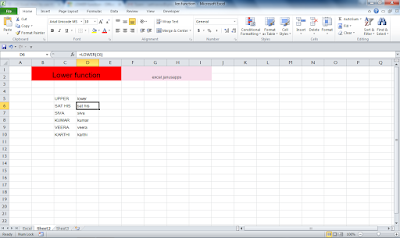
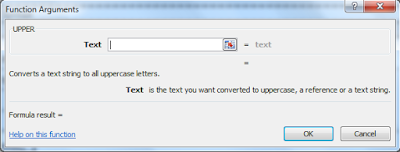
Home and Insert Ribbons
Home Ribbon
Home tab contains the most frequently used options such as cut-copy-paste, font formatting, alignment, Number, Conditional formatting, etc. All the options are used to format the data.Clip board
This group contains frequently used commands: Cut, Copy, Paste and Format painter. Clipboard option allows us to collect text and graphic items and paste it.Font
We use this option to change the font style and font-size. We can make it bold, italic and underline. Also, this group contains border styles, fill color, font color.Alignment
We use this option to change the alignment of cell’s text to the right, left and middle. Also, we can subject the text to top, bottom, and middle alignment. In this group, we have Wrap text option to adjust and make the text visible within a cell, and we can also merge 2 or more cells, using merge option.Number
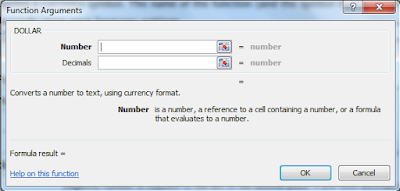
We use this option to change the number formatting into General, Percentage, Currency, Date, Time, Fraction etc. We can increase and decrease the decimal and convert the number into accounting number.Styles
In this option, we have Conditional Formatting, Format as Table and Cell Styles. Conditional formatting is used to highlight the cell or range on the basis of conditions. Format as table is having ready made table format and Cell styles feature different types of built-in styles that are a combination of Font style, Font color and Fill color.Cells
We use this option to insert or delete cells, rows, columns and sheets. Also, we have format option to adjust the height, width of cells or range. Using this option, we can hide or un hide the range, protect the workbook, rename the sheet name, fill the tab color, move or copy to sheets, lock the cells.Editing
This option has Auto Sum feature to return the total of numbers and move the text to right, left, up and down, Clear the format, content, comments and hyperlink; sort the data and find and select option.Insert Ribbon
We use Insert tab to insert the picture, charts, filter, hyperlink etc. We use this option to insert the objects in Excel. To open the insert tab, press shortcut keys Alt+N.Tables
We use this option to insert the dynamic table, Pivot table and recommended table. Pivot table is used to create the summary of report with the built-in calculation, and we have option to make our own calculation. Tables make it easy to sort, filter and format the data within a sheet. This option is also having recommended table that means on the basis of data, we can just insert the table as per the Excel’s recommendation.Illustration
We use this option to insert the Pictures, Online Pictures, Shapes, Smart Art and Screenshot. It means if we want to insert any image, we can use Illustration feature..Charts
Charts is very important and useful function in Excel. In excel, we have different and good numbers of ready made chart options. We have 8 types of different charts in Excel:- Column, Bar, Radar, Line, Area, Combo, Pie and Bubbles chart. We can insert pivot chart as well as Recommended chart, and if we don’t know which chart we should insert for the data, we can use this option to full fill the requirement.Spark lines
Spark line is a very tricky and useful option added by Microsoft Excel. On the basis of a range, it can visualize the trends in a single cell as charts. We have 3 different types of cell charts:- Line, Column and Win/Loss chart.Filters
We use this option to filter data visually and filter dates interactively. We have 2 options: Slicers and Timeline. We use Slicer to make the fast and easier to filter tables, Pivot tables, Pivot Charts and cube functions. Timeline makes it faster and easier to select time periods in order to filter Pivot Tables, Pivot Charts and Cube function.Links
We use this option to create the link in the document for the quick access to webpage and files.We can also use it to access different locations in the document.
Symbols
We use this option to insert the symbols and equation. Equation is used to insert the common mathematical equations to your document and also we can add equation byusing the mathematical symbols. We use Symbols to insert the symbols which are not on
the keyboard and, to create the equation,